
Please note that printk is a function which is defined in kernel, and it behaves similar to the printf in the IO library.
Using dmesg command, we can see the output from the sample Kernel module. Similarly, when the module is removed with rmmod, module_exit macro will be invoked, which will call the hello_exit. When a module is inserted into the kernel, the module_init macro will be invoked, which will call the function hello_init. Now that we have our hello.ko file, we can insert this module to the kernel by using insmod command as shown below. Insert or Remove the Sample Kernel Module The above will create hello.ko file, which is our sample Kernel module. Make: Leaving directory `/usr/src/linux-headers-3.5.0-19-generic' Make: Entering directory `/usr/src/linux-headers-3.5.0-19-generic' Make -C /lib/modules/3.5.0-19-generic/build M=/home/lakshmanan/a modules Use the make command to compile hello world kernel module as shown below. Make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean Make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules The following makefile can be used to compile the above basic hello world kernel module. So be careful with what you write in a kernel module. Warning: All kernel modules will operate on kernel space, a highly privileged mode. Printk(KERN_INFO "Cleaning up module.\n") Return 0 // Non-zero return means that the module couldn't be loaded. MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A Simple Hello World module") #include // included for _init and _exit macros #include // included for all kernel modules Next, create the following hello.c module in C programming language.
#Linux kernel modules install#
# apt-get install build-essential linux-headers-$(uname -r) 2. Depending on your distro, use apt-get or yum. Write a Simple Hello World Kernel Module 1. Refer to modprobe commands for more detailed examples. Modprobe is an intelligent command which will load/unload modules based on the dependency between modules. modprobe – Add or Remove modules from the kernel

You cannot remove a module which is already used by any program. Rmmod command will remove a module from the kernel.

Vermagic: 3.5.0-19-generic SMP mod_unload modversions 686 4. # modinfo /lib/modules/3.5.0-19-generic/kernel/fs/squashfs/squashfs.koįilename: /lib/modules/3.5.0-19-generic/kernel/fs/squashfs/squashfs.koĭescription: squashfs 4.0, a compressed read-only filesystem Modinfo command will display information about a kernel module as shown below. # insmod /lib/modules/3.5.0-19-generic/kernel/fs/squashfs/squashfs.ko Insmod command will insert a new module into the kernel as shown below. Lsmod command will list modules that are already loaded in the kernel as shown beblow. Utilities to Manipulate Kernel Modules 1.
#Linux kernel modules how to#
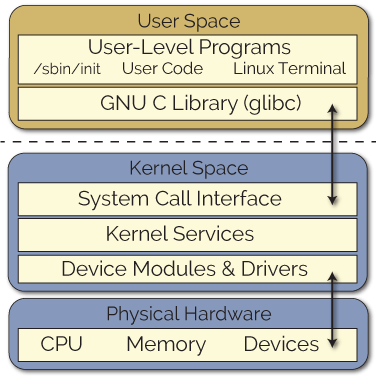
This tutorial explains how to write a Kernel module using a simple Hello World example. On a normal linux system, the kernel modules will reside inside /lib/modules//kernel/ directory.Įarlier we discussed how to compile a kernel from the source.
#Linux kernel modules drivers#
When those drivers are not needed, we can unload only that specific driver, which will reduce the kernel image size. Most of the drivers are implemented as a Linux kernel modules. Kernel modules offers an easy way to extend the functionality of the base kernel without having to rebuild or recompile the kernel again. Kernel modules are piece of code, that can be loaded and unloaded from kernel on demand.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
